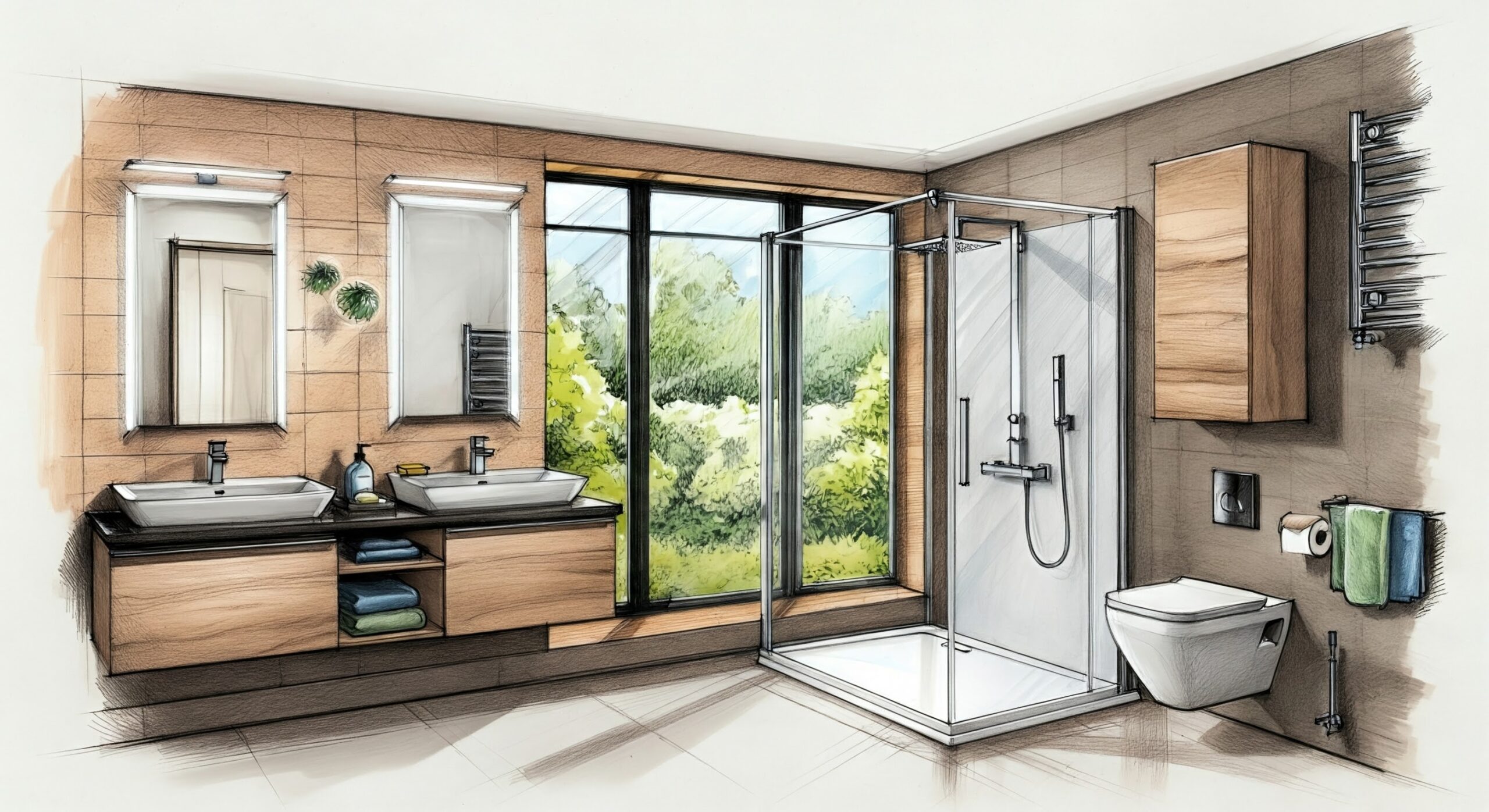
Bathrooms are essential spaces in residential and commercial architecture, serving both hygienic and aesthetic purposes. Their design demands meticulous attention to comfort, durability, hygiene, and visual cohesion, going beyond mere fixture selection [1]. This article delves into the creation of functional and enduring bathroom spaces, with a particular focus on optimizing layouts, selecting fixtures and furnishings, and utilizing durable finishes for shower cabinets. We will explore how advanced materials, ergonomic principles, and sustainable practices can be integrated to create bathrooms that are both beautiful and environmentally responsible.
Space Requirements and Layout
Ergonomic Optimization
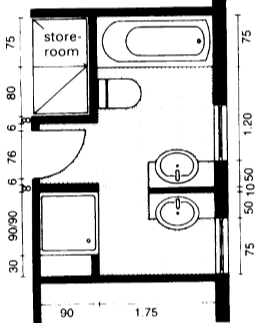
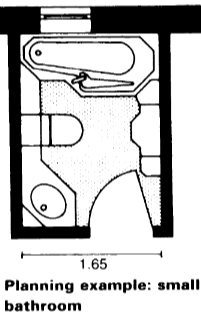
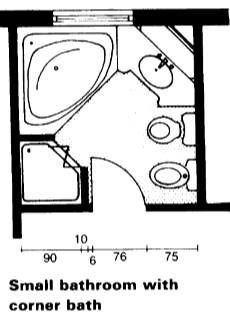
- Clearances: Adhering to spatial standards is crucial for ensuring comfortable and unobstructed movement within the bathroom. A minimum of 60 cm of clearance should be provided in front of toilets and 75 cm in front of sinks for ease of use [2].
- Zoning Strategies: Separating wet zones (showers, bathtubs) from dry zones (vanities, toilets) enhances water management and simplifies cleaning routines [3]. This separation can be achieved through physical barriers like glass partitions or through changes in floor level.
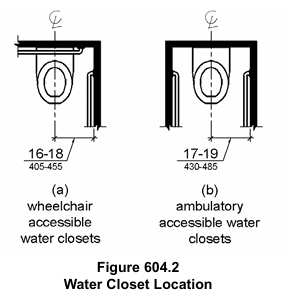
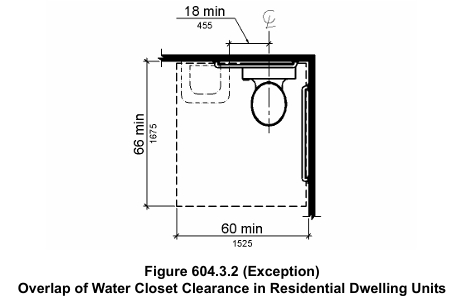
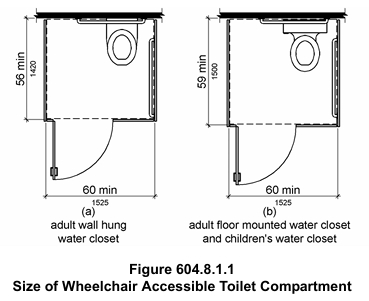
- Accessibility: Designing bathrooms with accessibility in mind is essential for creating inclusive spaces [4]. Incorporating features like wider doorways (at least 1000 mm), roll-in showers with no thresholds, and grab bars near toilets and showers ensures that the bathroom can be easily adapted to accommodate users with mobility challenges. A clear floor space circle with a diameter of 1500 mm should be provided within the bathroom to allow for maneuverability [5].
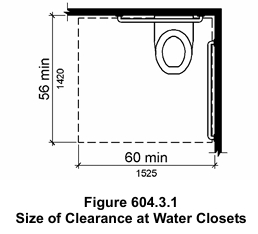
Fixture Placement
- Toilets: Toilets should ideally be aligned with plumbing stacks to minimize installation complexity and potential for leaks [6]. Wall-mounted systems enhance space efficiency and simplify cleaning by eliminating the need for a floor-mounted base.
- Sinks and Vanities: Sinks should be installed at ergonomic heights, typically between 80-85 cm, to accommodate users of varying heights [7]. Ample countertop space around the sink is essential for toiletries and daily essentials.
- Showers and Bathtubs: Shower enclosures should have a minimum dimension of 90×90 cm to ensure comfortable movement [8]. In larger bathrooms, freestanding bathtubs can serve as striking focal points, adding a touch of luxury and visual interest.
Optimal Fixtures and Furniture
Toilets
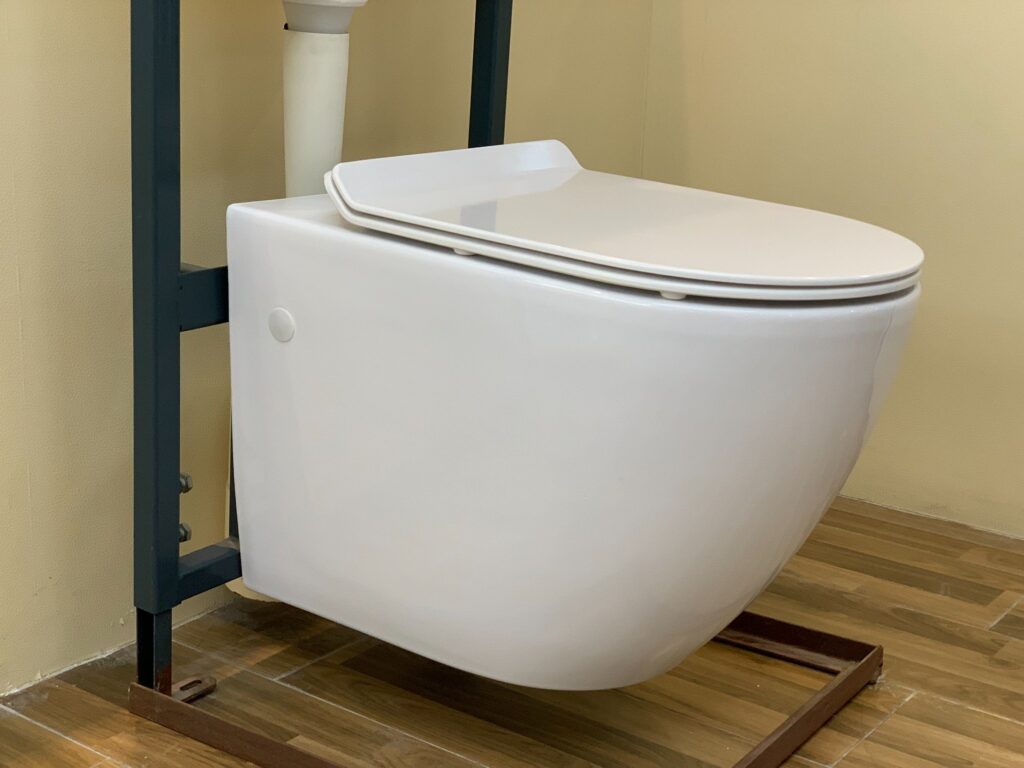





- Water-Saving Models: Dual-flush toilets are a prime example of water-efficient fixtures that conserve water without compromising performance [9]. Low-flow toilets and water-less urinals are other options to consider.
- Smart Features: Integrating bidet functionality, heated seating, and automated cleaning systems elevates both hygiene and user comfort. These features can also contribute to water conservation by reducing the need for toilet paper [10].
- Toilet Types: One-piece toilets offer a sleek, modern aesthetic and are easier to clean due to their seamless design. Two-piece toilets are more traditional and may be more budget-friendly.
Sinks and Faucets


- Integrated Designs: Vanities with integrated sinks and concealed storage maximize spatial utility, particularly in compact bathrooms [11]. This helps to maintain a clean and uncluttered look while providing ample storage for toiletries and other essentials.
- High-Performance Faucets: Durable and leak-proof faucets are essential for long-term performance. Brass and stainless-steel options, equipped with ceramic disc cartridges, are known for their longevity and resistance to wear and tear [12].
- Sink Materials: Porcelain and ceramic sinks are popular choices due to their durability, affordability, and ease of cleaning. Glass sinks offer a contemporary look, while natural stone sinks add a touch of luxury.
Showers
- Fixture Variety: Rain showers provide a luxurious and immersive experience, while handheld shower-heads offer flexibility for accessibility and cleaning [13]. Combination systems that include both fixed and handheld options offer the best of both worlds.
- Enclosure Systems: Frame-less tempered glass enclosures create a sleek and modern aesthetic while resisting staining and simplifying cleaning [14]. Consider using low-iron glass to minimize the greenish tint often found in standard tempered glass.
- Shower-heads: Water-saving shower-heads with flow restrictors can significantly reduce water consumption without sacrificing performance. Look for shower-heads with multiple spray settings to cater to different preferences.
Furniture and Storage
- Moisture-Resistant Materials: Bathroom furniture should be constructed from materials that can withstand high humidity levels. Marine-grade plywood or MDF with high-pressure laminate finishes are excellent choices for cabinets and vanities [15].
- Adaptive Storage Solutions: Open shelving adds visual lightness while offering practical storage for towels and decorative elements. Closed cabinets with moisture-resistant finishes provide concealed storage for toiletries and cleaning supplies.
- Small Bathroom Solutions: In compact bathrooms, consider utilizing vertical space with wall-mounted cabinets or shelves. Recessed niches in shower walls can provide convenient storage for toiletries without encroaching on valuable floor space.
Faucets and Fixtures: Quality and Ratings
While aesthetics and budget are important considerations when selecting bathroom fixtures, prioritizing quality and durability can lead to long-term cost savings and a more satisfying user experience. Investing in well-made fixtures can result in fewer repairs, reduced water consumption, and enhanced hygiene.
Understanding Fixture Ratings
Different rating systems exist for commercial and residential fixtures, reflecting the varying demands and usage patterns in these settings. Commercial fixtures are typically designed to withstand heavier use and more frequent cleaning, while residential fixtures are geared towards everyday household use.
- Commercial Fixtures: These are often rated according to standards set by organizations like the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI)1 [16]. These standards ensure that fixtures meet specific performance criteria, such as flow rate, durability, and resistance to vandalism.
- Residential Fixtures: Residential fixtures may also have ratings, though they are often less stringent than those for commercial applications. These ratings may focus on water efficiency (e.g., WaterSense label), performance (e.g., maximum flow rate), and compliance with local plumbing codes.
Why Invest in Higher-Quality Fixtures?
While higher-quality fixtures may come with a higher initial cost, they often offer several advantages:
- Durability: Well-made fixtures are constructed from more robust materials and undergo rigorous testing to ensure longevity. This translates to fewer repairs and replacements over time.
- Water Efficiency: High-efficiency fixtures, such as low-flow toilets and faucets with aerators, can significantly reduce water consumption, leading to lower utility bills and a smaller environmental footprint [17].
- Hygiene: Fixtures with smooth, non-porous surfaces are easier to clean and less prone to harboring bacteria and other microorganisms. This is particularly important in bathrooms, where hygiene is paramount.
- User Experience: High-quality fixtures often offer smoother operation, better temperature control, and enhanced features that contribute to a more enjoyable user experience.
By carefully considering fixture ratings and investing in durable, high-performance options, homeowners and designers can create bathrooms that are not only functional and aesthetically pleasing but also sustainable and cost-effective in the long run.
| Feature | Commercial Fixtures | Domestic Fixtures |
|---|---|---|
| Durability Tests | – More rigorous testing for durability, high-traffic use, vandalism resistance, and water efficiency. – Often tested to meet specific industry standards (e.g., ASME A112.19.2/CSA B45.1 for faucets). | – Basic performance and safety testing. – May not be as extensively tested for high-volume use or extreme conditions. |
| Warranty | – Typically shorter warranties (1-5 years) due to the demanding environment. – Focus on functionality and replacement parts availability. | – Longer warranties (5-10 years or even lifetime) are common. – May cover finishes and other aesthetic aspects. |
| Manufacturing Specs & Standards | – Emphasis on durability, vandal resistance, and ease of maintenance. – Materials: Chrome-plated brass, stainless steel, solid surface materials. – Compliance with accessibility standards (ADA) is crucial. | – Wider range of materials and styles. – Materials: Brass, chrome, nickel, porcelain, ceramic, plastics. – May prioritize aesthetics and design variety over extreme durability. |
| Estimated Usage Life | – Designed for heavy use and frequent operation. – Expected lifespan: 5-15 years or more with proper maintenance. | – Designed for moderate use in a household setting. <br> – Expected lifespan: 5-10 years, but can last longer with proper care. |
| Water Efficiency | – Stricter regulations and standards for water conservation (e.g., low-flow toilets, faucets, and showerheads). – Sensor-operated fixtures are common to reduce water waste. | – Water efficiency is becoming increasingly important, but regulations may be less stringent. – WaterSense-labeled products are available for those seeking water savings. |
| Maintenance | – Designed for easy maintenance and repair. – Cartridges and other replaceable parts are readily available. | – May require more specialized tools or knowledge for repairs. – Parts availability can be an issue for older or discontinued models. |
| Cost | – Generally more expensive due to higher material quality, durability, and compliance with standards. | – Wider price range depending on style, materials, and features. |
| Aesthetics | – Focus on functionality and practicality. – Design is often simple and utilitarian. | – Wider variety of styles and finishes to match different bathroom designs. |
| Cycle Life | – High cycle life (hundreds of thousands or millions of cycles). – Tested to withstand frequent on/off operation. | – Lower cycle life (tens of thousands of cycles). – Suitable for typical household use. |
Durable and Hygienic Finishes for Shower Cabinets
Material Selection
- Advanced Tile Systems: Porcelain and ceramic tiles are popular choices for shower walls and floors due to their durability, water resistance, and wide range of styles [18]. Textured, slip-resistant finishes enhance safety by reducing the risk of slips and falls.
- Natural Stone: Granite and slate confer a premium aesthetic but require periodic sealing to prevent moisture infiltration and staining [19]. Natural stone can add a touch of luxury and create a spa-like atmosphere in the bathroom.
- Seamless Surfaces: Solid surface materials like acrylic or Corian® offer grout-free installations, minimizing the risk of mold and mildew growth [20]. These materials are also available in a variety of colors and patterns to complement any bathroom design.
Waterproofing Systems
- Comprehensive Membranes: Installing waterproof membranes beneath tiled surfaces is crucial for preventing water damage to the underlying structure [21]. These membranes create a barrier against moisture, protecting walls and floors from leaks and moisture intrusion.
- Epoxy Grouts: Epoxy grouts offer superior resistance to staining and moisture compared to traditional cement-based grouts [22]. They are an excellent choice for shower areas, as they inhibit mold and mildew growth and maintain their color and integrity over time.
Health and Hygiene
- Low-VOC Finishes: Selecting low-emission paints, adhesives, and sealants minimizes indoor air pollution and contributes to a healthier indoor environment [23]. VOCs (volatile organic compounds) are chemicals that can be released into the air and may have adverse health effects.
- Anti-Microbial Coatings: Surfaces treated with anti-microbial finishes inhibit the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms, enhancing hygiene and reducing the spread of germs [24]. These coatings can be applied to various bathroom surfaces, including walls, floors, and fixtures.
- Ventilation Systems: Efficient exhaust fans are essential for controlling humidity levels and preventing mold and mildew growth [25]. Proper ventilation helps to remove excess moisture from the air, ensuring a comfortable and healthy bathroom environment.
Architectural Enhancements
Lighting Design
- Natural Light: Maximizing natural light in bathrooms creates a bright and welcoming atmosphere [26]. Consider incorporating skylights, windows with privacy glazing, or strategically placed mirrors to enhance daylighting.
- Task Lighting: Adequate task lighting is essential for activities like shaving, applying makeup, and grooming. Wall-mounted sconces or backlit mirrors at vanities provide focused illumination, minimizing shadows and ensuring optimal visibility.
- Ambient Solutions: Dimmable recessed lighting allows for flexible illumination, catering to different moods and activities. Consider incorporating a variety of light sources, such as overhead fixtures, accent lights, and natural light, to create a layered and balanced lighting scheme.
- Accent Features: LED strip lights integrated under cabinetry or within architectural niches add a subtle and sophisticated ambiance. Accent lighting can highlight specific features, such as artwork, textured walls, or decorative elements.
Flooring Solutions
- Resilient Options: Slip-resistant porcelain tiles or luxury vinyl planks are excellent flooring choices for bathrooms due to their durability, water resistance, and ease of maintenance. These materials offer a wide range of styles and colors to complement any design aesthetic.
- Radiant Heating: Underfloor heating systems enhance comfort, especially in colder climates, by providing a gentle and even warmth underfoot [27]. This can create a spa-like experience and add a touch of luxury to the bathroom.
Accessory Integration
- Towel Warmers: Electrically heated towel warmers enhance both functionality and luxury, providing warm and dry towels after a shower or bath. They can also contribute to reducing humidity levels in the bathroom.
- High-Performance Mirrors: Anti-fog mirrors improve visibility and usability under humid conditions, preventing condensation from obstructing the reflection. These mirrors are particularly useful in shower areas or near vanities.
Conclusion
Designing bathrooms requires an interdisciplinary approach that integrates technical rigor with aesthetic sensitivity. The selection of fixtures, furnishings, and finishes must prioritize longevity, hygiene, and user comfort while aligning with broader architectural goals. Incorporating sustainable practices, such as water-saving fixtures and energy-efficient lighting, is essential for minimizing environmental impact. By thoughtfully considering accessibility needs, designers can create inclusive spaces that can be easily adapted to accommodate users with varying abilities. Durable finishes for shower cabinets, ergonomic layouts, and advanced material technologies underscore the necessity for precision in these intimate spaces. By synthesizing innovation and practicality, architects and designers can craft bathrooms that exceed mere functionality, becoming sanctuaries of relaxation and well-being.
References
[1] Ching, F. D. K. (2014). Architecture: Form, space, and order. John Wiley & Sons.
[2] Panero, J., & Zelnik, M. (2001). Human dimension and interior space: A source book of design reference standards. Watson-Guptill.
[3] De Chiara, J., & Callender, J. H. (2014). Time-saver standards for building types. McGraw-Hill Education.
[4] ADA National Network. (2024). ADA Standards for Accessible Design. [invalid URL removed]
[5] Access Board. (2010). Chapter 6: Plumbing Elements and Facilities.
[6] Harris, C. M. (2005). Dictionary of architecture & construction. McGraw-Hill.
[7] Tilley, A. R. (2004). The measure of man and woman: Human factors in design. John Wiley & Sons.
[8] Neufert, E., & Neufert, P. (2012). Architects’ data. John Wiley & Sons.
[9] EPA. (2024). WaterSense. https://www.epa.gov/watersense
[10] Yu, D. L., & Crump, D. (2015). Smart and sustainable built environments. Springer.
[11] Ching, F. D. K. (2007). Interior design illustrated. John Wiley & Sons.
[12] Dempsey, C. (2010). Plumbing: The ultimate guide to selection, installation, and repair. Creative Publishing international.
[13] Allen, E., & Iano, J. (2013). The perfect bath. Taunton Press.
[14] Beall, C. (2005). The bath: Beautiful and practical. Images Publishing.
[15] Spence, W. P. (2005). Construction materials, methods, and techniques. Cengage Learning.
[16] ASME. (2024). ASME Standards. https://www.asme.org/codes-standards/find-codes-standards
[17] Energy Information Administration. (2016). Energy efficiency in buildings. U.S. Department of Energy.
[18] Salvadori, M. (2002). Why buildings stand up: The strength of architecture. W. W. Norton & Company.
[19] Merritt, F. S., & Ricketts, J. T. (2003). Building design and construction handbook. McGraw-Hill.
[20] Groák, S. (1992). The illustrated guide to kitchen and bathroom design. Rodale Press.
[21] Straube, J. F. (2005). High-performance building enclosures: Design guide for commercial buildings. Building Science Press.
[22] Schubert, R. (2003). Construction defects and failures. McGraw-Hill.
[23] U.S. Green Building Council. (2024). LEED v4.1 for Building Design and Construction. https://www.usgbc.org/leed
[24] Russell, A. D., Hugo, W. B., & Ayliffe, G. A. J. (1999).2 Principles and practice of disinfection, preservation and sterilization. Blackwell Science.
[25] ASHRAE. (2017). ASHRAE handbook: Fundamentals. American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers.
[26] Robbins, C. L. (1986). Daylighting: Design & analysis. Van Nostrand Reinhold.
[27] Lechner, N. (2015). Heating, cooling, lighting: Sustainable design methods for architects. John Wiley & Sons.

